What does ASCE on rail mean?
In the world of rail transport and infrastructure, standards and specifications play a crucial role in ensuring safety, reliability, and interoperability. One commonly encountered term is "ASCE" – an acronym that holds significance in the realm of rail engineering.
1. Defining ASCE:
1.1 Acronym Breakdown:
ASCE stands for the American Society of Civil Engineers. This professional organization, founded in 1852, is dedicated to advancing the practice of civil engineering and establishing standards that promote the safety and efficiency of civil engineering projects, including rail infrastructure.
2. ASCE Standards in Rail Engineering:
2.1 ASCE 60 and ASCE 85:
The numbers following ASCE refer to specific standards within the organization's portfolio. In the context of rail engineering, ASCE 60 and ASCE 85 are two notable standards related to rail design.
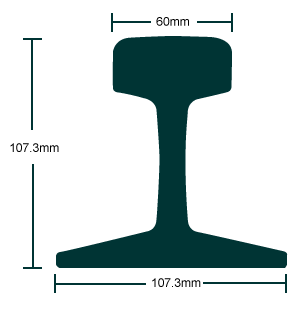
ASCE 60: This standard pertains to rail sections commonly used in the construction of railroad tracks. It includes specifications for the dimensions, weight, and other properties of the rail profile.
ASCE 85: This standard provides guidelines for the design and installation of rail turnouts, also known as switches or points. It covers the geometric and structural aspects of turnouts to ensure their proper functioning within a rail network.
3. Rail Profiles and Dimensions:
3.1 ASCE 60 Rail:
4. Turnout Design and Installation:
4.1 ASCE 85 Turnouts:
ASCE 85 provides comprehensive guidelines for the design and installation of turnouts. Turnouts are critical components in rail systems, facilitating the diversion of trains from one track to another. Proper design and construction are vital to ensuring the safety and efficiency of rail operations.
The standard covers aspects such as the layout and dimensions of turnouts, clearances, and the geometric relationships between different components. By adhering to ASCE 85, rail engineers can create turnouts that meet industry standards and contribute to a reliable and interconnected rail network.
5. Importance of Standards:
5.1 Safety and Interoperability:
5.2 Quality Assurance:
Following ASCE standards ensures a level of quality assurance in rail construction. Engineers, manufacturers, and operators can rely on these benchmarks to deliver rail components that meet the industry's expectations for durability and performance.
6. Global Relevance:
6.1 Adoption Beyond the U.S.:
ASCE on rail refers to standards set by the American Society of Civil Engineers, specifically ASCE 60 for rail sections and ASCE 85 for turnouts. These standards play a crucial role in ensuring the uniformity, safety, and efficiency of rail infrastructure in the United States and beyond. By adhering to these standards, rail professionals contribute to the creation of a reliable and interconnected rail network that meets the highest engineering and safety standards.
Featured content:How to detect 304 stainless steel plate?What Is the Difference Between Cast Aluminum and Die-Cast Aluminum?Differences Between Hydrated Lime and QuicklimeWhat is the silica fume?What is metal palisade fencing?Everything You Need to Know About Carbide Bar: FAQs AnsweredUltimate Guide to Customized Ground Tungsten Carbide Rods: Everything You Need to Know









Comments
Please Join Us to post.
0